What is Vitamin B12 and why is it important for children?
Vitamin B12, also known as cobalamin, is a crucial nutrient that helps maintain the health of nerve cells and blood cells, and is involved in the creation of DNA, the genetic material in cells. It’s particularly important for brain development in babies and young children.

How can I tell if my child has Vitamin B12 deficiency?

The symptoms of Vitamin B12 deficiency in children can be subtle and may include
- fatigue
- muscle weakness
- irritability
- digestive issues
- weight loss
- developmental delays.
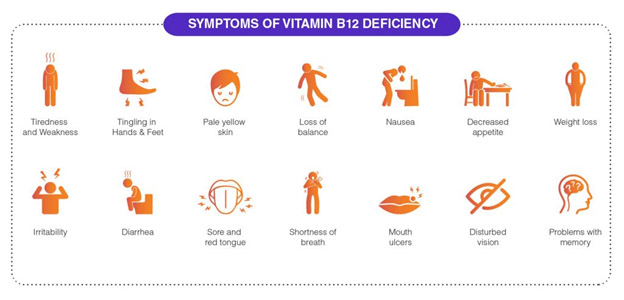
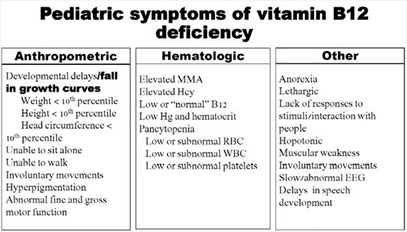
If you notice any of these symptoms, it’s important to consult your pediatrician
What causes Vitamin B12 deficiency in children?
Children can become deficient in Vitamin B12 if their diet lacks adequate sources of the vitamin, such as meat, dairy, and eggs. Conditions that affect the absorption of Vitamin B12, like Crohn’s disease, or a history of intestinal surgery, can also lead to deficiency. Additionally, infants can be affected if their mothers had low Vitamin B12 levels during pregnancy.
Can Vitamin B12 deficiency be prevented?
Yes, ensuring a balanced diet that includes foods rich in Vitamin B12, like fish, meat, poultry, eggs, milk, and fortified cereals, can prevent deficiency. For those on a vegan diet, B12 supplements or fortified foods are necessary.
How is Vitamin B12 deficiency treated in children?
Treatment typically involves increasing dietary intake of Vitamin B12 or providing supplements. In cases of severe deficiency or absorption issues, injections of Vitamin B12 may be required. Your pediatrician will guide you on the best course of action based on your child’s needs.

Are there any long-term effects of Vitamin B12 deficiency?
If left untreated, Vitamin B12 deficiency can lead to serious health concerns, including nerve damage and cognitive difficulties. However, with early detection and proper treatment, most children recover well and have no lasting effects.
Should I give my child Vitamin B12 supplements?
Supplementation should be considered for children with a diagnosed deficiency or those at risk, such as children following a strict vegan diet without fortified foods. Always consult with a healthcare provider before starting any supplements2.
How often should my child be tested for Vitamin B12 levels?
Testing frequency depends on individual risk factors and dietary intake. Discuss with your pediatrician to determine if and when testing is necessary for your child1.
Remember, this information is for educational purposes and should not replace professional medical advice. If you suspect your child has a Vitamin B12 deficiency, please consult your pediatrician for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan. Early intervention is key to managing and resolving this condition effectively.